|
Name: Opium poppy
Type: Opioid
AKA: Papaver somniferum

|
|
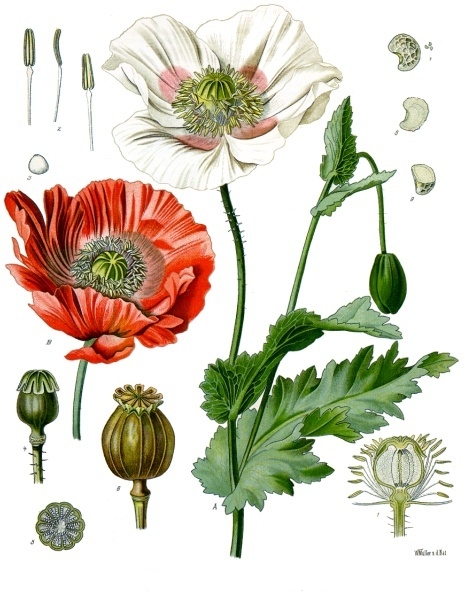
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
The opium poppy, Papaver somniferum, has been used for thousands of years for its psychoactive and medicinal properties. It is the source of opiates such as morphine and codeine and has played a significant role in medicine and drug culture.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Opium poppy is the source of several controlled substances, including morphine and heroin. It is regulated globally due to its potential for abuse and addiction. In the United States, its cultivation and processing are strictly controlled to prevent illicit drug production. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - II
Schedule II drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a high potential for abuse, with use potentially leading to severe psychological or physical dependence. These drugs are also considered dangerous. Some examples of Schedule II drugs are: combination products with less than 15 milligrams of hydrocodone per dosage unit (Vicodin), cocaine, methamphetamine, methadone, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), meperidine (Demerol), oxycodone (OxyContin), fentanyl, Dexedrine, Adderall, and Ritalin.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
The opium poppy is a plant used for producing opiates such as morphine and codeine. It has significant analgesic and sedative effects. Short-term use of opiates derived from opium poppy is effective for pain management, but long-term use can lead to addiction, tolerance, and severe health issues. Overdose risks include fatal respiratory depression. Safe use involves strict dosing and medical supervision. Recent research focuses on its role in medicine and associated risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
N/A
 |
|
VIII. Culture
The opium poppy has profound historical and cultural significance, dating back thousands of years. It is mentioned in ancient Sumerian texts and has been used in various cultures for its psychoactive and medicinal properties. The poppy played a crucial role in the development of early medicine and was central to historical events such as the Opium Wars. In modern culture, it is at the heart of the opioid crisis, with ongoing debates about its medical use and potential for abuse. The opium poppy is symbolic in various cultural, religious, and medical contexts.
 |
