|
Name: Opium preparations - 100 mg/(100 ml or 100 gm)
Type: Opioid
AKA: Parepectolin, Kapectolin PG, Kaolin Pectin P.G.

|
|
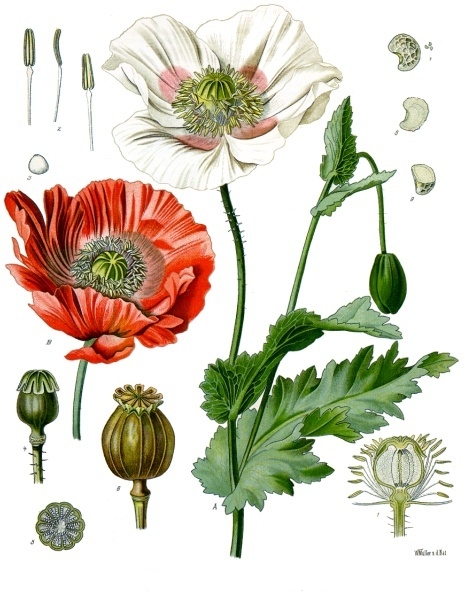
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
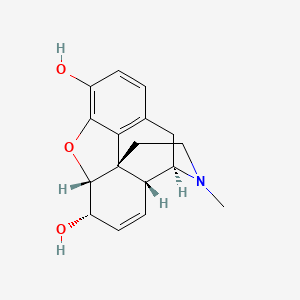
|
|
IV. History
Opium, derived from the opium poppy, has been used since ancient times for its analgesic and sedative properties. Its preparations, including tinctures and extracts, have played a significant role in medicine throughout history. The evolution of opium preparations reflects changing practices in pain management and addiction treatment.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Opium preparations are tightly regulated under the Schedule II classification in the US, allowing limited medical use but reflecting high abuse potential. Globally, opium is controlled under international drug conventions. The UNODC emphasizes strict regulation to prevent illegal trade and misuse. Trends show ongoing efforts to balance medical needs with preventing abuse and illicit production.
US Federal Schedule - V
Schedule V drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with lower potential for abuse than Schedule IV and consist of preparations containing limited quantities of certain narcotics. Schedule V drugs are generally used for antidiarrheal, antitussive, and analgesic purposes. Some examples of Schedule V drugs are: cough preparations with less than 200 milligrams of codeine or per 100 milliliters (Robitussin AC), Lomotil, Motofen, Lyrica, Parepectolin.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Opium preparations contain morphine and codeine, acting as depressants. They lead to sedation, decreased heart rate, and respiratory depression. Short-term effects include effective pain relief and euphoria, while long-term use can cause addiction, tolerance, and severe health problems. Overdose risks involve fatal respiratory depression. Safe use requires strict medical supervision. Recent research focuses on addiction management and therapeutic improvements.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Opium preparations affect opioid receptors, causing euphoria and cognitive impairment. Immediate effects include mood enhancement and pain relief, while long-term use can result in dependence and psychological issues such as depression. Effects last several hours, with significant mental health risks with chronic use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Opium preparations have been used for centuries for their analgesic and psychoactive properties. Historically, opium has played a significant role in medicine, trade, and culture, from ancient civilizations to the Opium Wars of the 19th century. Modern preparations, although less common, continue to be used in some medicinal contexts. The cultural significance of opium lies in its profound impact on global history, medicine, and society. Its use has led to critical developments in pharmacology, public health policies, and international relations. Media coverage often highlights the historical importance of opium and its enduring legacy in contemporary drug policy and addiction treatment.
 |
