|
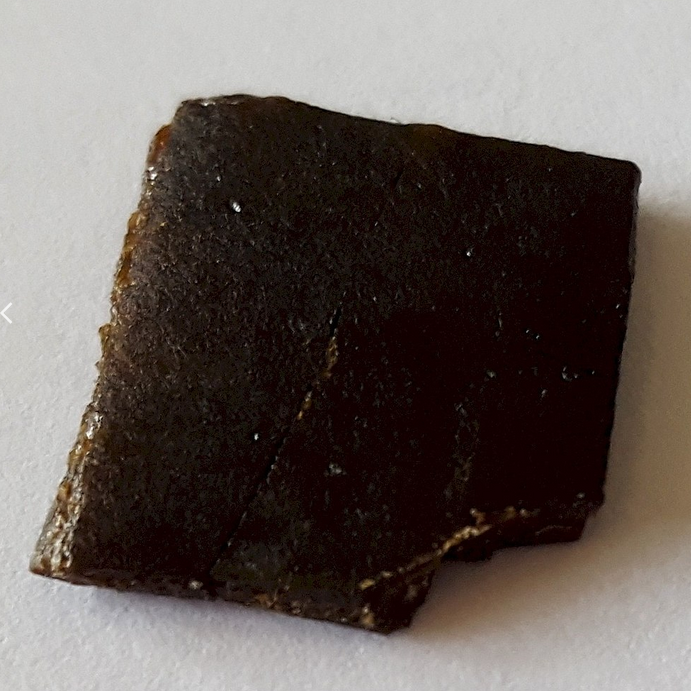
Name: Opium tincture
Type: Opioid
AKA: Laudanum

|
|
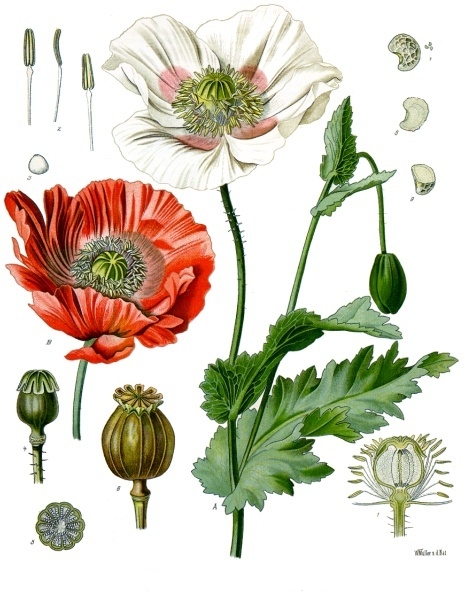
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
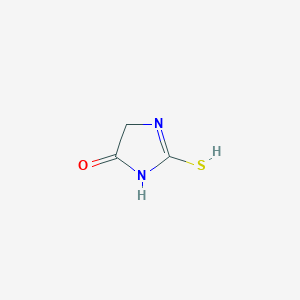
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Opium tincture, also known as laudanum, has been used since the 16th century for its analgesic and antitussive properties. It was historically used to treat pain and cough but has been largely replaced by other medications due to its addictive potential.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Opium tincture, a preparation of opium used for medicinal purposes, is regulated due to its narcotic content. In the United States, it is controlled under the Controlled Substances Act, with similar regulations worldwide to prevent misuse and protect public health. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - II
Schedule II drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a high potential for abuse, with use potentially leading to severe psychological or physical dependence. These drugs are also considered dangerous. Some examples of Schedule II drugs are: combination products with less than 15 milligrams of hydrocodone per dosage unit (Vicodin), cocaine, methamphetamine, methadone, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), meperidine (Demerol), oxycodone (OxyContin), fentanyl, Dexedrine, Adderall, and Ritalin.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Opium tincture is an alcoholic solution of opium used for pain relief. It acts as a downer, causing significant sedation and analgesia. Short-term use is effective for managing severe pain, but long-term use may lead to dependence and tolerance. Overdose risks include severe respiratory depression and potential death. Safe use requires careful dosing and medical supervision. Recent research examines its efficacy and safety compared to other opioids.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Opium tincture, containing opium alkaloids, affects mu-opioid receptors, leading to significant euphoria and sedation. Immediate effects include mood elevation and pain relief, lasting several hours. Long-term use may result in severe addiction, cognitive impairments, and mood disturbances. Research emphasizes its potency and risks of psychological dependence and cognitive effects.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Opium tincture, also known as laudanum, has historical significance dating back to ancient Egypt and was widely used in the 19th century. It was utilized for its analgesic properties and as a cough suppressant. Its cultural impact includes its role in early medicine and its association with addiction. Proponents valued its pain-relieving properties, while opponents highlight its potential for misuse and addiction. Its use is both medicinal and recreational, reflecting historical and modern issues with opioid treatment.
 |
