|
Name: oxandrolone (17-alpha-methyl-17-beta-hydroxy-2-oxa-5-alpha-androstan-3-one)
Type: Androgenic steroid
AKA: Anavar, Lonavar, Oxandrin, Provitar, Vasorome

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
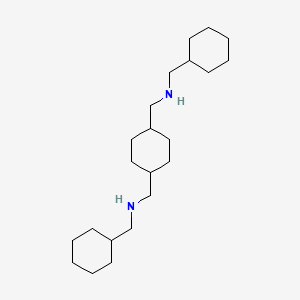
|
|
IV. History
Oxandrolone, first synthesized in 1962 by Raphael Pappo at Searle Laboratories, is an anabolic steroid used to promote weight gain and muscle growth. It is notable for its lower androgenic effects compared to other anabolic steroids. Oxandrolone has been used in medical settings to treat conditions like muscle wasting and is also popular among bodybuilders and athletes, although its use is restricted in competitive sports.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Oxandrolone, an anabolic steroid, is regulated as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions due to its potential for misuse in sports. In the US, it is classified under Schedule III. Globally, it faces similar controls to prevent abuse and manage health risks associated with anabolic steroids.
US Federal Schedule - III
Schedule III drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Oxandrolone, an anabolic steroid, is used to enhance muscle growth. As an upper, it increases muscle mass and strength. Short-term effects include improved physical performance and muscle growth, while long-term use can cause cardiovascular issues, liver damage, and hormonal imbalances. Overdose risks involve severe health complications. Safe use involves medical supervision, and recent findings highlight its efficacy and associated risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Oxandrolone, an anabolic steroid, impacts mood and aggression through androgen receptors. Immediate effects include mood enhancement and increased aggression, with long-term use leading to psychological issues and cognitive impairments. Research focuses on its effects on mental health and hormonal balance.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Oxandrolone, an anabolic steroid, is used to promote muscle growth and enhance athletic performance. Its cultural significance is tied to its role in bodybuilding and sports, as well as the broader discussions about steroid use. Oxandrolone reflects ongoing debates about performance enhancement, including health risks, ethical considerations, and regulatory challenges. Its role in the cultural narrative is one of performance enhancement and the complex issues surrounding anabolic steroid use.
 |
