|
Name: oxymesterone (17-alpha-methyl-4,17-beta-dihydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one)
Type: Androgenic steroid
AKA: Anamidol, Balnimax, Oranabol, Oranabol 10

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
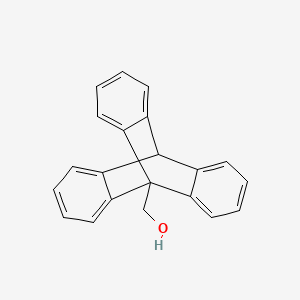
|
|
IV. History
Oxymesterone, a synthetic anabolic steroid, was developed in the 1960s. It was created to enhance muscle growth and performance, primarily in sports and bodybuilding. Its use has been controversial due to health risks and potential for abuse. Regulatory measures have been implemented to control its use, reflecting broader concerns about anabolic steroids and their impact on health and athletic performance.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Oxymesterone, an anabolic steroid, is illegal for non-medical use in the US and classified under the Anabolic Steroid Control Act. It is similarly banned in many countries due to its potential for abuse in sports and bodybuilding. Regulatory bodies enforce strict measures to control the distribution and use of anabolic steroids to prevent health risks and doping.
US Federal Schedule - III
Schedule III drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Oxymesterone is an anabolic steroid used to enhance muscle growth. It increases muscle mass and strength but causes hormonal imbalances and potential liver damage, acting as an upper. Short-term use may improve performance, while long-term use poses significant health risks including cardiovascular issues and liver damage. Overdose risks include severe hormonal disturbances and health complications. Safe use involves medical supervision and adherence to recommended doses. Recent research focuses on its muscle-enhancing effects and health risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Oxymesterone is a synthetic anabolic steroid that alters hormone balance in the brain. Immediate effects include increased aggression, mood swings, and enhanced focus. Long-term use can result in anxiety, depression, and increased aggressive behavior. Chronic use is associated with cognitive impairments and potential mood disorders. Recent research indicates anabolic steroids can lead to structural brain changes.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Oxymesterone is an anabolic steroid used to enhance muscle mass and strength, classifying it as an upper. Short-term use promotes muscle growth and improves recovery times, while long-term use can lead to liver damage, cardiovascular issues, and hormonal imbalances. Overdose risks include severe liver toxicity and cardiovascular complications. Safe usage involves medical supervision and dosages generally under 50 mg per day. Recent findings emphasize the importance of monitoring for adverse effects. Physical signs include increased muscle mass and potential liver enzyme abnormalities.
 |
