|
Name: Paraldehyde
Type: Sedative-hypnotic
AKA: Paral

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
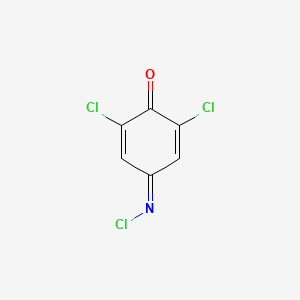
|
|
IV. History
Paraldehyde, a sedative and hypnotic, has been used since the 19th century. It was once a common treatment for insomnia and anxiety but has largely been replaced by newer medications due to its side effects and the development of more effective treatments.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Paraldehyde is a sedative and anxiolytic used in medical settings. It is controlled in some regions due to its potential for misuse and dependence. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - IV
Schedule IV drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Some examples of Schedule IV drugs are: Xanax, Soma, Darvon, Darvocet, Valium, Ativan, Talwin, Ambien, Tramadol.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Paraldehyde is a sedative and hypnotic with CNS depressant effects. It causes sedation, reduced heart rate, and constricted pupils. Short-term use can manage severe anxiety and seizures, but long-term use may lead to tolerance, dependence, and liver damage. Overdose risks include severe sedation and respiratory depression. Safe use requires adherence to dosing guidelines. Recent research highlights its historical use and current limited application due to side effects.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Paraldehyde is a sedative-hypnotic producing sedation, anxiolysis, and anticonvulsant effects. Immediate effects include reduced anxiety, improved mood, and sedation. Long-term use can result in dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms. Chronic use is associated with cognitive impairment and potential development of depressive disorders. Recent studies indicate potential for abuse and mental health impacts.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Paraldehyde, a sedative and hypnotic, was used extensively in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It is mentioned in historical medical texts for its role in treating seizures and insomnia. In modern times, its use has declined due to the development of safer alternatives. It has minimal cultural significance today, but was once noted in medical practices and early pharmaceutical developments. Proponents valued its effectiveness, while modern critics point to its side effects and obsolescence in favor of newer drugs.
 |
