|
Name: Pentedrone (-alpha-methylaminovalerophenone)
Type: Synthetic cathinone
AKA: 2-(methylamino)-1-phenylpentan-1-one) (Positional Isomers: 3-methylethcathinone (3-MEC), 4-ethylmethcathinone (4-EMC), 4-methylbuphedrone (4-MeMABP;4-MeBP), 3, 4-dimethylmethcathinone (3, 4-DMMC), N-ethylbuphedrone (NEB), N-ethyl-N-methylcathinone(EMC))

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
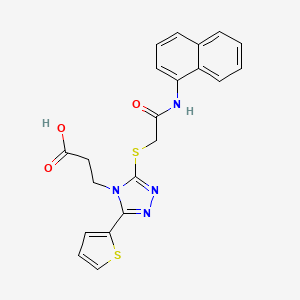
|
|
IV. History
Pentedrone is a synthetic cathinone first identified in the 2010s. It is a stimulant with effects similar to methcathinone and other related substances. Pentedrone gained popularity as a recreational drug, particularly in the context of 'bath salts'. Its potential for abuse and adverse effects led to its classification as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Pentedrone, a synthetic stimulant, is often regulated under analog acts due to its structural similarity to other controlled substances. In the US, it is not explicitly listed but could fall under the Federal Analogue Act if considered similar to Schedule I or II stimulants. Globally, its legal status varies, with increasing restrictions on synthetic stimulants reflecting concerns about their abuse potential and health risks.
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Pentedrone, a synthetic stimulant, is part of the cathinone family. As an upper, it increases heart rate, energy, and euphoria. Short-term effects include heightened alertness and mood elevation, while long-term use may cause cardiovascular problems and addiction. Overdose risks involve severe agitation, hallucinations, and cardiovascular events. Safe use involves cautious dosing and monitoring. Recent studies indicate its stimulant effects and the need for regulation due to potential abuse and health risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Pentedrone, a stimulant, affects neurotransmitter systems, causing increased energy and euphoria. Psychological effects include heightened alertness and potential anxiety. The effects last 3-6 hours, with risks of dependence and long-term mental health issues. Research is ongoing into its safety profile and potential for abuse.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Pentedrone, a synthetic cathinone, gained prominence in the early 21st century as part of the 'bath salts' phenomenon. It is often associated with recreational drug use in club scenes and among individuals seeking potent stimulant effects. The substance’s cultural impact is linked to the rise of synthetic drugs marketed as legal alternatives, which exploit regulatory gaps. Pentedrone’s unpredictable and sometimes dangerous effects have made it a subject of public health concern. The substance reflects broader societal issues related to drug regulation, safety, and the evolving landscape of synthetic psychoactive substances.
 |
