|
Name: Pentobarbital & noncontrolled active ingred.
Type: Barbiturate
AKA: FP-3

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
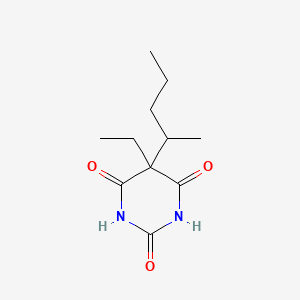
|
|
IV. History
Pentobarbital, used in combination with non-controlled active ingredients, has been used for its sedative and anesthetic properties. The combination forms were developed to enhance efficacy and manage various medical conditions, though it is now less commonly used due to safety concerns.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Pentobarbital and non-controlled active ingredients are often regulated separately. Pentobarbital is a controlled substance due to its potential for abuse, while non-controlled ingredients are regulated based on their use and safety.
US Federal Schedule - III
Schedule III drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Pentobarbital is a barbiturate used for sedation and anesthesia. It acts as a downer, causing sedation and reduced consciousness. Short-term use is effective for sedation, but long-term use can lead to dependence and cognitive issues. Overdose risks include severe sedation and respiratory depression. Safe use requires careful dosing and medical supervision. Recent research examines its efficacy and safety compared to other sedatives.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Pentobarbital and its non-controlled active ingredients, barbiturates, affect GABA-A receptors to provide sedation and mood alteration. Immediate effects include relaxation and cognitive impairment, with long-term use potentially causing dependence and cognitive decline. Research examines its safety and psychological impacts.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Pentobarbital is a barbiturate with a long history of use as a sedative and anesthetic. It gained cultural significance in the mid-20th century as a widely used medication. Modern discussions focus on its use in euthanasia and capital punishment, with significant ethical debates. Proponents of its use in euthanasia argue for the right to die with dignity, while opponents raise moral and ethical concerns. Its cultural impact is substantial, reflecting broader societal debates about end-of-life issues and the ethics of capital punishment. Its use is both medicinal and controversial, depending on the context.
 |
