|
Name: Pipradrol
Type: Stimulant
AKA: Detaril, Stimolag Fortis

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
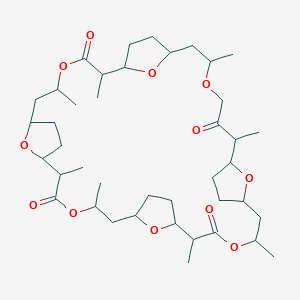
|
|
IV. History
Pipradrol is a stimulant drug that was first developed in the 1950s. It was used to treat conditions such as narcolepsy and ADHD. Pipradrol works by increasing the levels of norepinephrine and dopamine in the brain. Its use has declined due to the development of newer medications with better safety profiles. Pipradrol is now rarely prescribed and is considered a controlled substance in many countries.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Pipradrol, a stimulant with potential for abuse, is regulated under controlled substance laws in various countries. In the US, it could fall under analog laws if considered similar to controlled stimulants. Globally, its legal status varies, with increasing restrictions reflecting concerns about its stimulant effects and potential for misuse.
US Federal Schedule - IV
Schedule IV drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Some examples of Schedule IV drugs are: Xanax, Soma, Darvon, Darvocet, Valium, Ativan, Talwin, Ambien, Tramadol.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Pipradrol, a stimulant, enhances alertness and concentration. As an upper, it increases heart rate and energy levels. Short-term effects include euphoria and improved focus, while long-term use may lead to dependence and cardiovascular issues. Overdose risks include severe agitation and cardiovascular events. Safe use involves limiting doses. Recent research highlights its stimulant properties and concerns over potential abuse and health risks.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Pipradrol, a stimulant, affects neurotransmitter systems to increase alertness and euphoria. Psychological effects include heightened focus and potential anxiety. The duration of effects is 4-6 hours, with risks of dependence and cognitive impairments. Recent research examines its safety profile and historical use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Pipradrol, a stimulant introduced in the mid-20th century, was used to treat conditions like narcolepsy and ADHD. Its cultural significance is tied to the broader history of stimulant use in medicine and the evolving understanding of cognitive enhancement. Pipradrol represents the early efforts to manage attention and wakefulness disorders, reflecting the ongoing quest for effective treatments. However, due to its potential for abuse and the development of safer alternatives, its use has declined. Pipradrol's role in the cultural narrative is one of historical interest in the development of stimulant medications.
 |
