|
Name: Promethazine
Type: Antihistamine and antiemetic
AKA:
|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
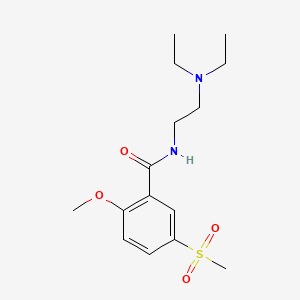
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
|
|
IV. History
Promethazine, an antihistamine and sedative, was developed in the 1940s. It is used for allergy relief and as a sedative. Its role in treating motion sickness and nausea is well-established, and it continues to be used in various medical applications.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Promethazine is an antihistamine used for its sedative effects. It is controlled due to its potential for misuse and impact on mental health. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - V
Schedule V drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with lower potential for abuse than Schedule IV and consist of preparations containing limited quantities of certain narcotics. Schedule V drugs are generally used for antidiarrheal, antitussive, and analgesic purposes. Some examples of Schedule V drugs are: cough preparations with less than 200 milligrams of codeine or per 100 milliliters (Robitussin AC), Lomotil, Motofen, Lyrica, Parepectolin.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Promethazine is an antihistamine used for allergy relief and sedation. It causes drowsiness, reduced heart rate, and constricted pupils. Short-term use alleviates allergy symptoms and induces sleep, while long-term use may cause cognitive impairment and dependence. Overdose risks include severe sedation and respiratory depression. Safe use involves adhering to prescribed doses. Recent research emphasizes its effectiveness for allergy relief and the risks of misuse.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Promethazine, an antihistamine, affects H1 receptors and may also interact with dopamine receptors, leading to sedation and mood changes. Immediate effects include drowsiness and mood relaxation, lasting several hours. Long-term use may result in cognitive impairments and mood disturbances. Research focuses on its use as an antihistamine and associated risks of cognitive effects with prolonged use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Promethazine is an antihistamine with sedative properties, used to treat allergies and motion sickness. Its cultural significance lies in its use for various medical conditions and its potential for misuse. Media coverage often addresses the balance between its therapeutic uses and the risks of sedation and potential misuse. Promethazine is used medicinally and is part of broader discussions about allergy treatments, sedation, and the potential for drug misuse.
 |
