|
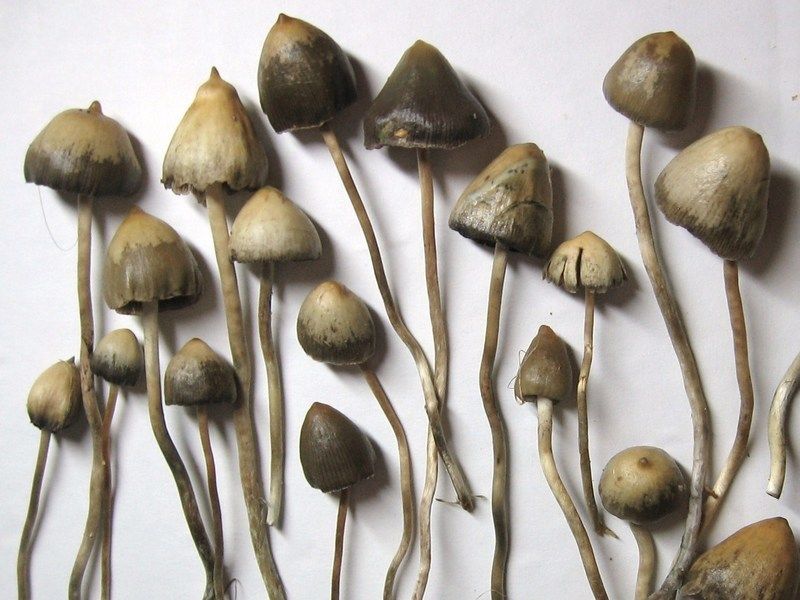
Name: Psilocyn
Type: Hallucinogen
AKA: Psilocin, Magic mushrooms, shrooms, shroomies, caps

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
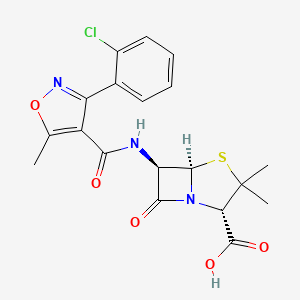
|
|
IV. History
Psilocyn, a psychoactive compound, is a natural derivative of psilocybin found in various psychedelic mushrooms used since ancient times in Mesoamerican cultures for spiritual rituals. It gained scientific attention in the 1950s and 1960s during the psychedelic research era and remains a subject of interest for its potential therapeutic uses.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Psilocyn is a naturally occurring psychedelic compound found in certain mushrooms. It is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance in the U.S. due to its hallucinogenic properties. Internationally, it faces similar restrictions, with trends showing increasing regulation to manage psychedelic drug use. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - I
Schedule I drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Some examples of Schedule I drugs are: heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana (cannabis), 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy), methaqualone, and peyote.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Psilocyn is a psychoactive compound found in certain mushrooms. It induces altered perception, euphoria, and hallucinations. Short-term effects include altered states of consciousness and mood enhancement, while long-term use may lead to psychological changes. Overdose risks are minimal but can include anxiety and disorientation. Safe use involves moderation and a controlled environment. Recent research focuses on its therapeutic potential and effects on mental health.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
N/A
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Psilocyn, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushrooms, has a long history of use in indigenous cultures, particularly in Central and South America. It was used in religious and spiritual ceremonies by the Aztecs and other Mesoamerican cultures. In modern times, psilocyn has gained attention for its potential therapeutic benefits in treating depression and anxiety. The cultural significance of psilocyn is marked by its association with the psychedelic movement of the 1960s and its current resurgence in psychedelic research. Media coverage often highlights its potential for mental health treatment and the ongoing debates about its legalization and medicinal use. Proponents advocate for its therapeutic potential, while opponents raise concerns about its safety and potential for abuse.
 |
