|
Name: Quinine
Type: Antimalarial agent
AKA: Quinine, Cinchona

|
|
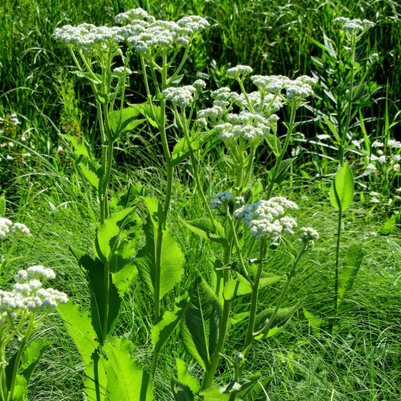
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
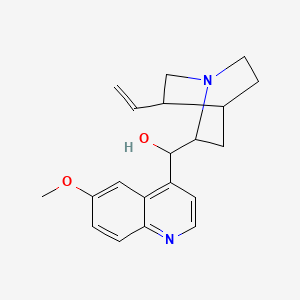
|
|
IV. History
Quinine, derived from the bark of the cinchona tree, has been used for centuries to treat malaria. It was a crucial development in medicine and continues to play a role in the treatment of malaria.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Quinine, an antimalarial drug, is legally regulated globally. In the US, it is available by prescription for specific medical uses. Some countries restrict its sale to prevent misuse, such as in tonic water for treating leg cramps. The WHO includes quinine on its list of essential medicines, reflecting its importance but also the need for controlled distribution to prevent abuse and side effects.
Key US Federal Policies:
Quinine is regulated by the FDA, with strict guidelines for its use due to potential side effects. It is approved for treating malaria and certain muscle cramps.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Quinine is an alkaloid used historically to treat malaria. It acts as a central nervous system stimulant and can also have sedative effects at high doses. Short-term use can effectively treat malaria, but excessive use can lead to tinnitus, nausea, and potential toxicity. Long-term use may cause vision problems and cardiovascular issues. Overdose risks include severe toxicity and organ damage. Safe use involves careful dosing and monitoring. Recent research explores its efficacy in malaria treatment and potential side effects.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Quinine, an antimalarial and muscle relaxant, affects mood and cognitive function. Immediate effects include mood stabilization and cognitive enhancement, while long-term use can lead to psychological issues such as anxiety and cognitive decline. Research indicates potential for mental health disturbances with chronic use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Quinine is a natural compound used for its antimalarial and muscle relaxant properties. Short-term use treats malaria and muscle cramps, while long-term use can lead to cinchonism, characterized by symptoms like tinnitus and nausea. Overdose risks include severe cardiovascular and neurological effects. Safe dosages are medically prescribed, typically under 600 mg per day. Recent research supports its efficacy in treating malaria but warns of potential side effects. Physical effects include reduced fever and muscle relaxation.
 |
