|
Name: Salicylic Acid
Type: Topical agent
AKA: Aspirin, Willow Bark

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
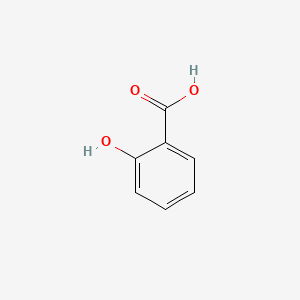
|
|
IV. History
Salicylic acid, a compound derived from willow bark, has been used in medicine for centuries. It is the precursor to aspirin and has been studied for its anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Salicylic acid is a common compound used in medicines and cosmetics, particularly for treating acne and other skin conditions. It is legal and widely used, with regulations focusing on its concentration and safety in products. [Source: UNODC].
Key US Federal Policies:
Salicylic acid is regulated by the FDA, with guidelines for its safe use in both medicinal and cosmetic applications. Aspirin products must meet specific labeling requirements to ensure proper usage and dosage.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Salicylic acid is a common topical treatment used for its exfoliating and anti-inflammatory properties. It is effective for treating acne and other skin conditions. Short-term use is generally safe, but excessive use may cause skin irritation or dryness. Safe use involves following recommended application guidelines. Recent research highlights its efficacy in treating skin conditions and its safety profile.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Salicylic acid does not have psychoactive effects. It is primarily used to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and lower fever.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Salicylic acid is a beta hydroxy acid widely used in dermatology for its exfoliating and anti-inflammatory properties. Short-term use treats acne and skin conditions, while long-term use is generally safe but may cause skin irritation. Overdose risks are low, typically leading to skin redness and peeling. Safe usage involves topical application with concentrations up to 2% for general skincare. Recent findings support its efficacy in acne treatment. Physical effects include improved skin texture and reduced acne.
 |
