|
Name: Suvorexant
Type: Hypnotic
AKA: ['MK-4305', '[(7R)-4-(5-chloro-1', '3-benzoxazol-2-yl)-7-methyl-1', '4-diazepan-1-yl][5-methyl-2-(2H-1', '2', '3triazol-2-yl)phenyl]methanone']

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
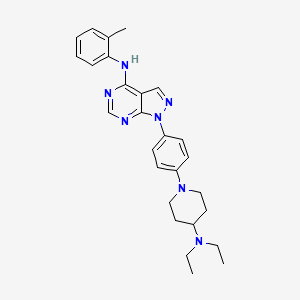
|
|
IV. History
Suvorexant, a dual orexin receptor antagonist, was developed in the 2010s for the treatment of insomnia. Its introduction marked a new approach to managing sleep disorders by targeting specific brain receptors involved in regulating wakefulness.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Suvorexant, an orexin receptor antagonist used to treat insomnia, is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance in the US, allowing limited medical use. It is approved for medical use in many countries. Regulatory bodies like the FDA ensure its safe prescription. The UNODC does not classify it as a major concern. Trends show a steady acceptance for its therapeutic use.
US Federal Schedule - IV
Schedule IV drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Some examples of Schedule IV drugs are: Xanax, Soma, Darvon, Darvocet, Valium, Ativan, Talwin, Ambien, Tramadol.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Suvorexant is an orexin receptor antagonist used to treat insomnia. It causes sedation and may lead to reduced heart rate. Short-term use effectively improves sleep quality, while long-term use is generally safe with minimal risk of dependency. Overdose risks are low, but excessive use may cause dizziness and impaired motor function. Safe use involves following prescribed dosages. Recent research supports its efficacy in managing insomnia and highlights its safety profile.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Suvorexant, an orexin receptor antagonist, is used to treat insomnia. It affects orexin systems, promoting sleep and reducing wakefulness. Immediate effects include improved sleep onset and maintenance. Long-term use is generally safe, though occasional drowsiness or cognitive impairment may occur. Recent studies highlight its efficacy in treating insomnia with minimal long-term psychological impacts.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Suvorexant is a dual orexin receptor antagonist used to treat insomnia, classifying it as a downer. Short-term use improves sleep onset and maintenance, while long-term use is generally well-tolerated but may lead to dependence. Overdose is rare but can cause severe drowsiness and sedation. Safe dosages are medically prescribed, typically 10-20 mg per night. Recent research supports its efficacy and safety in chronic insomnia treatment. Physical effects include drowsiness, dizziness, and potential next-day sedation.
 |
