|
Name: testolactone (13-hydroxy-3-oxo-13,17-secoandrosta-1,4-dien-17-oic acid lactone)
Type: Androgenic steroid
AKA: Teolit, Teslac

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
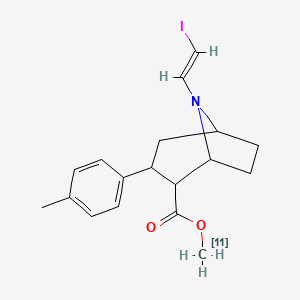
|
|
IV. History
Testolactone, introduced in the 1970s, is a steroid hormone used in hormone therapies. It is known for its role in treating breast cancer and other hormone-related conditions, reflecting its significance in endocrine therapy.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Testolactone, an anabolic steroid, is regulated as a controlled substance due to its potential for misuse in sports. In the US, it is classified under Schedule III.
US Federal Schedule - III
Schedule III drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Testolactone is an anabolic steroid used to enhance muscle growth. As an upper, it promotes muscle mass and strength. Short-term effects include increased physical performance, while long-term use may lead to cardiovascular issues and hormonal imbalances. Overdose risks involve severe health complications. Safe use requires medical supervision. Recent research focuses on its effectiveness and potential side effects.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Testolactone, an anabolic steroid, impacts mood and aggression through androgen receptors. Immediate effects include mood enhancement and increased aggression, while long-term use can lead to psychological issues such as depression and cognitive impairments. Research highlights risks of mood swings and mental health issues with extended use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Testolactone is a synthetic non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor used in the treatment of breast cancer, classifying it as neither an upper nor a downer. Short-term use reduces estrogen production and slows tumor growth, while long-term use can cause mild side effects like nausea and fatigue. Overdose risks are low, with large doses potentially leading to gastrointestinal upset. Safe dosages are medically prescribed, typically under 250 mg per day. Recent research supports its use in hormone-related cancer treatments. Physical effects include reduced estrogen levels and potential tumor shrinkage.
 |
