|
Name: Thebaine
Type: Opioid
AKA: Precursor of many narcotics

|
|
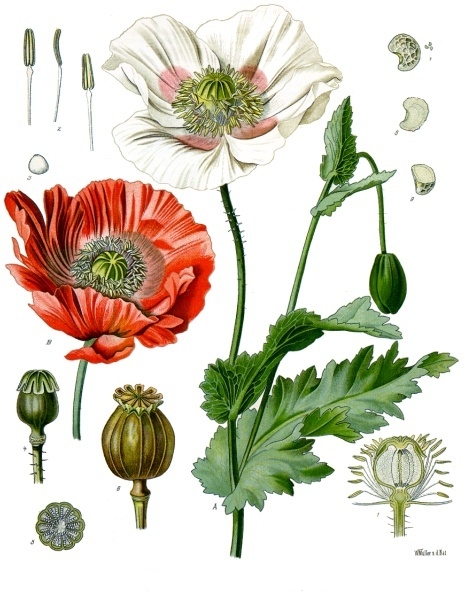
II. Natural Derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
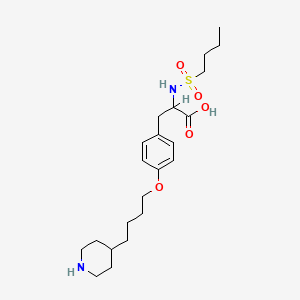
|
|
IV. History
Thebaine, an alkaloid derived from the opium poppy, has been used since the 19th century. It is a precursor in the synthesis of various opioids and has played a significant role in opioid research.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Thebaine is an opioid alkaloid used in the synthesis of other opioids. It is controlled due to its role in opioid production and its potential for misuse. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - II
Schedule II drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a high potential for abuse, with use potentially leading to severe psychological or physical dependence. These drugs are also considered dangerous. Some examples of Schedule II drugs are: combination products with less than 15 milligrams of hydrocodone per dosage unit (Vicodin), cocaine, methamphetamine, methadone, hydromorphone (Dilaudid), meperidine (Demerol), oxycodone (OxyContin), fentanyl, Dexedrine, Adderall, and Ritalin.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Thebaine is an alkaloid found in the opium poppy with stimulant and convulsant properties. It acts as an upper, increasing alertness but can also cause agitation and seizures. Short-term use may lead to increased energy and alertness, but long-term use can result in addiction and neurological damage. Overdose risks include convulsions and severe agitation. Safe use involves controlled dosing. Recent research examines its potential for use in opioid synthesis and its safety profile.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Thebaine is an opioid with stimulant and analgesic effects. Short-term use can lead to mood elevation and sedation, while long-term use may result in addiction, cognitive impairments, and mood disorders. Research focuses on its impact on opioid receptors and psychological risks.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Thebaine, an alkaloid found in the opium poppy, has historical significance as a precursor to many modern opioids. It has been used in traditional medicine, but its primary importance lies in its role in the synthesis of drugs like oxycodone and buprenorphine. Modern cultural discussions focus on its role in the pharmaceutical industry and its connection to the opioid crisis. Proponents include pharmaceutical companies and researchers, while opponents are concerned about its potential for misuse. Its use is medicinal, with significant impact on modern medicine and public health.
 |
