|
Name: Tiletamine & Zolazepam Combination Product
Type: Dissociative anesthetic
AKA: Telazol
|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
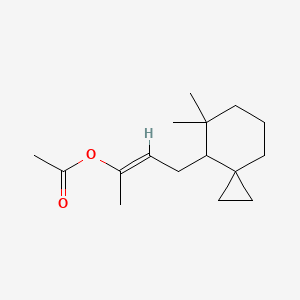
|
|
IV. History
Tiletamine and zolazepam are anesthetic agents combined into a single product for use in veterinary medicine. Developed in the 1980s, this combination provides both anesthetic and muscle relaxant effects. It is used primarily in animal surgery and sedation, known for its effectiveness in inducing anesthesia and its safety profile in veterinary practices.

|
|
V. Legal Information
The Tiletamine & Zolazepam combination product is a controlled substance in many jurisdictions due to its use as an anesthetic and its potential for abuse. In the US, it is regulated under Schedule III. Globally, its legal status reflects its use in veterinary medicine and efforts to manage misuse.
US Federal Schedule - III
Schedule III drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Tiletamine and zolazepam, combined in a veterinary anesthetic, induce sedation and dissociation. As downers, they cause significant sedation and altered consciousness. Short-term effects include dissociation and relaxation, while long-term use may lead to psychological issues. Overdose risks involve severe sedation and respiratory depression. Safe dosing requires medical supervision. Recent findings focus on its use in anesthesia and the need for careful monitoring.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Tiletamine and zolazepam, a combination anesthetic, affect NMDA and GABA-A receptors. Immediate effects include sedation and dissociation, with long-term use potentially causing cognitive impairments and psychological issues. Research highlights its use in anesthesia and potential cognitive effects.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
The combination of tiletamine and zolazepam is used in veterinary medicine as an anesthetic for large animals. Historically, the development of anesthetics revolutionized both human and veterinary medicine, enabling complex surgeries and pain management. In modern times, this combination is critical in animal care, ensuring humane treatment during procedures. Discussions around veterinary anesthetics often focus on animal welfare and the advancements in medical practices that improve the quality of life for animals. This combination product is a staple in veterinary practices, representing the intersection of medical science and animal care.
 |
