|
Name: Vinbarbital
Type: Barbiturate
AKA: Delvinal, vinbarbitone

|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative

|
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
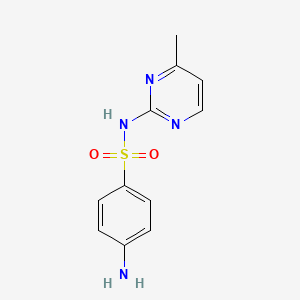
|
|
IV. History
Vinbarbital, a barbiturate, was first synthesized in the 1960s. It was used as a sedative and anticonvulsant. Its history includes its use in various medical contexts and its eventual decline due to the development of newer medications with better safety profiles.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Vinbarbital is a barbiturate derivative with sedative properties. Historically, it was used in medical treatments but is now less common due to the rise of newer medications with fewer side effects. In the U.S., it is classified as a controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act, with international controls reflecting its potential for abuse. Trends show a move towards stricter regulation of barbiturates due to their high addiction potential. [Source: UNODC].
US Federal Schedule - III
Schedule III drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Schedule III drugs abuse potential is less than Schedule I and Schedule II drugs but more than Schedule IV. Some examples of Schedule III drugs are: products containing less than 90 milligrams of codeine per dosage unit (Tylenol with codeine), ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Vinbarbital is a barbiturate used as a sedative. It induces drowsiness and reduces heart rate. Short-term effects include effective sedation, while long-term use may lead to dependence and cognitive issues. Overdose risks include severe sedation and respiratory depression. Safe use requires careful medical dosing. Recent research emphasizes its efficacy as a sedative and the risks associated with barbiturate use.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Vinbarbital, a barbiturate, affects GABA receptors, causing sedation and mood alteration. Immediate effects include anxiety reduction and mood enhancement, while long-term use can result in dependence and psychological issues such as depression. Effects last several hours, with significant mental health risks with chronic use.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Vinbarbital is a barbiturate used for its sedative and hypnotic effects. The history of barbiturates reflects their early use in treating anxiety, insomnia, and seizure disorders, as well as their decline due to the development of safer alternatives. Vinbarbital's cultural significance lies in its representation of the evolution of sedative medications and the ongoing search for effective treatments with minimal side effects. The use of barbiturates is often discussed in the context of their potential for dependence and overdose. Media coverage typically highlights the risks associated with barbiturate use and the historical context of their development and regulation.
 |
