|
Name: Zolpidem
Type: Hypnotic
AKA: Ambien, Ivadal, Stilnoct, Stilnox
|
|
II. Natural Derivative
Synthetic substance, no natural derivative
 |
|
III. Chemical Profile (IUPAC name)
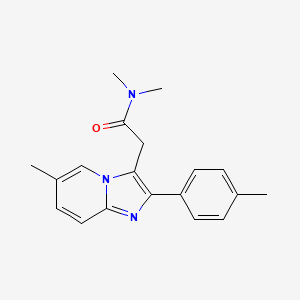
|
|
IV. History
Zolpidem, introduced in 1992 by Searle Pharmaceuticals, is a sedative-hypnotic used to treat insomnia. It belongs to the imidazopyridine class of drugs and is known for its selective action on GABA receptors. Zolpidem revolutionized sleep medicine with its efficacy and safety profile, becoming a widely prescribed medication for short-term insomnia treatment.

|
|
V. Legal Information
Zolpidem, a medication used for insomnia, is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance in the US due to its potential for abuse. Globally, it is similarly regulated to manage its use in treating sleep disorders while preventing misuse.
US Federal Schedule - IV
Schedule IV drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined as drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence. Some examples of Schedule IV drugs are: Xanax, Soma, Darvon, Darvocet, Valium, Ativan, Talwin, Ambien, Tramadol.
Key US Federal Policies:
Controlled Substances Act. Public Law: Public Law 91-513 (text can be found on GovInfo) (https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa). Date enacted: October 27, 1970.
|
|
VI. Physical Effects
Zolpidem, a sedative-hypnotic, is used to treat insomnia. As a downer, it induces drowsiness and improves sleep. Short-term effects include enhanced sleep quality and reduced insomnia, while long-term use can lead to dependence and cognitive impairment. Overdose risks involve severe sedation and respiratory issues. Safe dosing typically ranges from 5-10 mg nightly. Recent research highlights its effectiveness for sleep disorders and risks of misuse.  |
|
VII. Psychological Effects
Zolpidem, a sedative-hypnotic, enhances GABA-A receptor activity, providing rapid onset of sleep. Immediate effects include sedation and cognitive impairment, with long-term use potentially leading to dependence and cognitive issues. Research explores its efficacy for sleep disorders and risks of cognitive decline.
 |
|
VIII. Culture
Zolpidem, commonly known as Ambien, is a widely used prescription medication for insomnia. Since its approval in the 1990s, it has become a cultural icon in discussions about sleep health and pharmaceutical dependence. Historically, sleep aids have ranged from natural remedies to barbiturates, with each era's solutions reflecting societal attitudes towards sleep and health. Modern use of zolpidem has been linked to incidents of 'sleep-driving' and other unusual behaviors, leading to media scrutiny and legal cases. Celebrities have openly discussed their use and misuse of the drug, highlighting issues of addiction and the pressures of modern life.
 |
